
ZED-F9P module
u-blox F9 high precision GNSS module
Technology
|
22 Jul 2024
The new message authentication feature
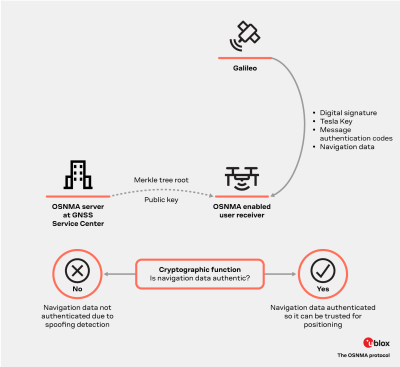
Galileo OSNMA (Open Service Navigation Message Authentication) is currently in the final stages of testing. This resilient feature is expected to become attractive for high-end and mass-market GNSS receivers.
Galileo OSNMA is a GNSS-embedded feature that ensures secure end-to-end transmissions from Galileo satellites to GNSS receivers. Designed to prevent GNSS spoofing attacks, the feature assures GNSS receivers that the Galileo navigation message comes from the system itself and has not been tampered with, enhancing the GNSS receiver’s robustness by increasing its ability to detect spoofing attempts.
With the data authentication that Galileo OSNMA provides, it is possible to:
Galileo is the first and so far the only GNSS constellation to offer authentication to civilian users.
Automotive (ADAS). Galileo OSNMA promises to be a critical feature for the security of vehicles with ADAS functionalities. One of the primary use cases in ADAS is the combination of GNSS’s absolute position and velocity data with relative position information from ranging sensors and cameras. In addition, processing GNSS timing information for interconnected sensors, cameras, and processing units is crucial to maintain synchronization. This synchronized timing is essential for real-time data processing and decision-making. Given the safety and security criticality of these GNSS-based functions, Galileo OSNMA authentication can be a fundamental element of the ADAS security architecture, supporting compliance with standards such as ISO 21434.
Timing. Critical infrastructure, such as telecommunications networks, data centers, and power grids, rely on GNSS for timing and synchronization. These applications require extremely high levels of security because failures can provoke severe consequences. OSNMA helps protect these critical applications against GNSS spoofing attacks.
Numerous servers and devices operate in concert in data centers. Synchronizing timing ensures efficient data processing, which helps prevent disruptions and bottlenecks. Galileo OSNMA empowers telecom providers and data center operators to achieve consistent and synchronized time across their infrastructure. It supports the ever-increasing demands of modern communications and computing systems.
Further applications: surveying, fishing regulations, and agricultural subsidies. Galileo OSNMA may find applications in these different environments. Government organizations may mandate the use of Galileo OSNMA to ensure the authenticity of survey points, preventing surveyors from falsifying data. Regulators of the fishing industry may require fishing boats to submit navigation logs authenticated by Galileo OSNMA to verify that they have only fished in designated areas, thereby protecting against falsified records. Another application could be the monitoring of agricultural subsidies. Under the Common Agricultural Policy, Galileo OSNMA could be used to reduce fraud by ensuring that farmers do not manipulate data to improperly collect subsidies.
For engineers:
For other users: In general, users at various levels should be able to trust that their data is authenticated, providing an additional layer of protection. For example, if automated systems cannot authenticate the data, they could go into a safe state, just like a jamming detector. Governments can also ensure that a user is not hacking the system. Another example could be an insurance company using the feature to monitor driver behavior.
Galileo OSNMA is knocking on our doors. This feature’s arrival is imminent, and it will significantly improve the security of GNSS receivers. u-blox uses every technological tool at its disposal to make its GNSS receivers even more secure – you can count on it.